Forest Vegetation types - TH5
TH5 — Beech / Sarsaparilla / Leaf litter
Fagus grandifolia / Aralia nudicaulis
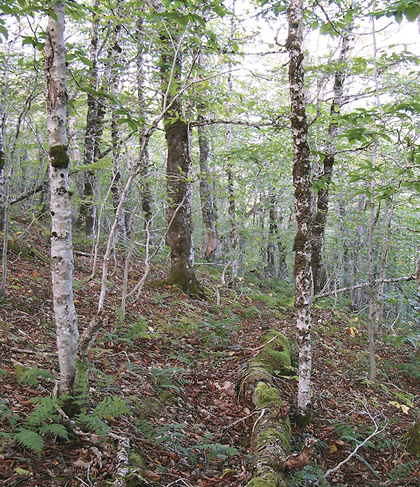 |
Twelve O'Clock Mountain, Inverness County |
Concept: This late successional Vegetation Type (VT) has an overstory dominated by beech that can sometimes dominate the shrub layer. Other than beech, below canopy ground cover is typically sparse, aside from leaf litter on the forest floor. Prior to the introduction of beech bark canker, the long-lived and shade-tolerant nature of beech allowed this ecosystem to develop old forest characteristics maintained by gap disturbance. However, Beech / Sarsaparilla / Leaf litter is now relatively uncommon in the province.
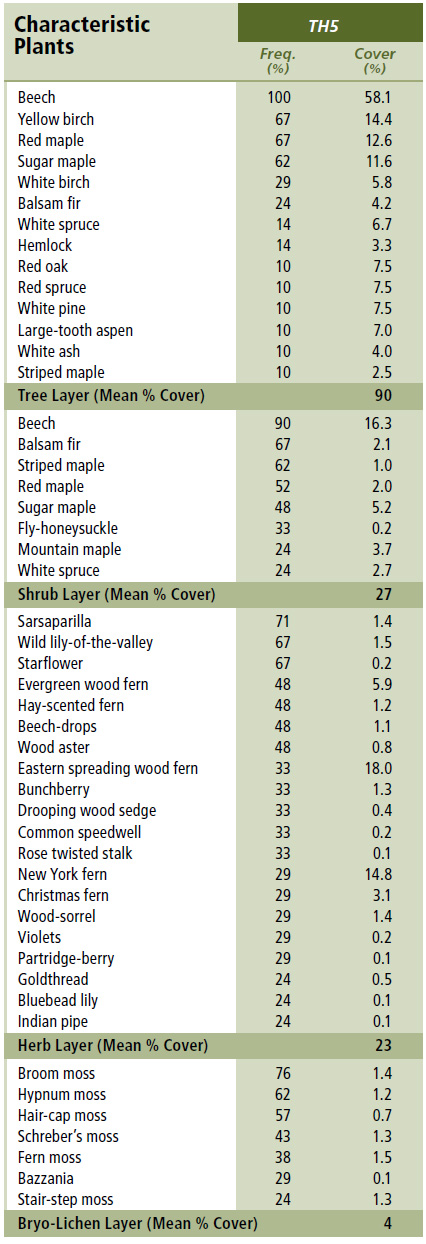
Vegetation: Beech is the dominant overstory tree, with minor amounts of sugar maple, red maple and yellow birch. Species diversity and coverage in the shrub and herb layers are typically very low – a condition likely related to the phytotoxicity (toxicity to plants) of beech litter leachate. Some shrub and herb cover can be found under mixed species portions of the canopy. Understory species include regenerating trees, striped maple, sarsaparilla and a variety of ferns. Beech drops, a saprophytic plant, is also usually found. As in other tolerant hardwood VTs, the bryophyte layer is poorly developed, with moss cover generally restricted to tree trunks, stones and downed woody material.
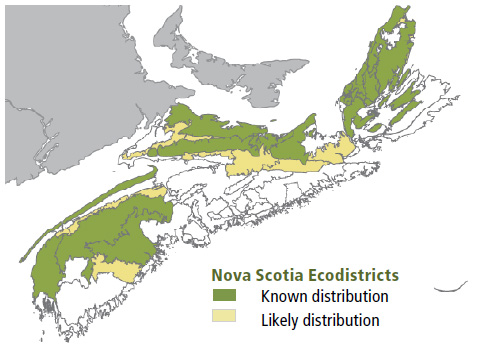
Environmental Setting: TH5 is found on dry to fresh, nutrient-medium soils derived from glacial till or colluvium. This VT is mainly found in hilly topography associated with the Nova Scotia Uplands ecoregion and the North Mountain and South Mountain ecodistricts. It can also occur on the crests of drumlins. Beech / Sarsaparilla / Leaf litter is relatively uncommon in New Brunswick and on Prince Edward Island mature stands of this VT are absent.
Successional Dynamics: TH5 is a late successional, climatic climax VT dominated by beech. Excluding harvesting, stand-level disturbance events are rare with gaps or small patches usually created by individual tree mortality, wind, or ice damage. This VT has been significantly impacted by beech bark canker, and its future in the Acadian forest is uncertain. Trends suggest that other shade-tolerant hardwoods will eventually establish on these sites. At present most TH5 sites are even-aged, but eventual replacement by sugar maple, red maple and yellow birch will lead to a more uneven-aged condition. Progression to TH1 (Sugar maple / Hay-scented fern), TH2 (Sugar maple / New York fern – Northern beech fern) or IH7 (Red maple / Hay-scented fern – Wood sorrel) is likely.
Ecological Features: This closed canopy hardwood forest typically occurs in large patches. Beech scale disease, introduced from Europe in the 1890s, has decimated tree quality and mast production in these forests. Beech is very shade-tolerant and the impact of the disease has reduced this species to an intermediate or understory species, altering its ecological role in stand structure and dynamics. However, beech is still is an important food source for bears, small mammals, blue jays, finches, woodpeckers and yellow-bellied sapsuckers. Cavities in tree stems, often created when branches break off, provide nesting and denning habitat. Beech-drops, a parasitic plant on beech roots, are often found wherever the tree grows. There is evidence of some genetic resistance to beech scale, thus mature, clean, trees may present conservation and restoration opportunities. These forests may host a variety of spring ephemeral plants, which take advantage of early spring sunlight before tree leaf out.
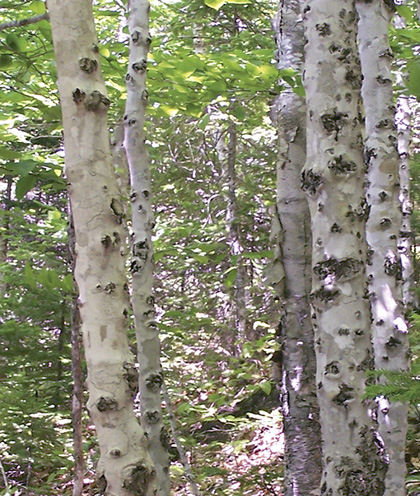 |
| Diseased beech |
Distinguishing Features: Located on rapid to well drained soils of crests and upper slopes this hardwood forest is dominated by beech. Shrub and herb coverage is sparse and the forest floor is primarily beech leaf litter. Beech drops are common. Beech canker scars on all age classes of beech is usually evident.
| Slope Position: | Upper7 Middle2 Other1 |
Surface Stoniness: |
(Non - Slightly)5 (Very - Excessively)3 (Moderately)2 |
Bedrock Outcrop: |
(Non-rocky)8 (Slightly - Moderately)2 |
Elevation Range: |
69 - 357m |
Slope Gradient: |
Gentle4 Steep4 Level1 Moderate1 |
Aspect: |
North2 East4 South3 West1 |
Exposure: |
Mod. exposed4 Exposed3 Moderate2 Other1 |
Microtopography: |
Moderately4 Strongly3 Slightly2 Level1 |
Drainage: |
Well8 Rapid1 Other1 |
Soil Type: |
ST24 ST83 ST2-L1 Other2 |
Parent Material: |
Glacial till7 Colluvium2 Till/Bedrock1 |
Rooting Depth (cm): |
(<30)1 (30-45)2 (>45)6 nd1 |
Duff Thickness (cm): |
(0-5)3 (6-10)3 (11-20)3 nd1 |