The Economics and Statistics Division maintains archives of previous publications for accountability purposes, but makes no updates to keep these documents current with the latest data revisions from Statistics Canada. As a result, information in older documents may not be accurate. Please exercise caution when referring to older documents. For the latest information and historical data, please contact the individual listed to the right.
<--- Return to Archive
For additional information relating to this article, please contact:
March 19, 2021BANK OF JAPAN MONETARY POLICY Based on the current economic situation and the economic outlook, the Bank of Japan decided to maintain the negative interest rate of -0.1% on balances of financial institutions at the Bank. The Bank of Japan will also purchase a necessary amount of Japanese government bonds (JGBs) without setting an upper limit in order to keep the 10-year JGB yields at around zero per cent.
In addition, the Bank will actively purchase exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and Japan real estate investment trusts (J-REITs) so that their amounts outstanding will increase at annual paces with upper limit of about 12 trillion yen and about 180 trillion yen, respectively. The Bank will continue purchases of Commercial paper and corporate bonds with an upper limit on the amount of outstanding of about 20 trillion yen in total until the end of September 2021.
The Bank will continue with "Quantitative and Qualitative Monetary Easing (QQE) with Yield Curve Control," aiming to achieve the price stability target of 2 per cent, as long as it is necessary for maintaining that target in a stable manner. The Bank also noted that it will continue expanding the monetary base until the year-on-year rate of increase in the observed CPI (all items less fresh food) exceeds 2 per cent and stays above the target in a stable manner.
In response to COVID-19, the Bank will continue to support financing of firms and maintain financial market stability through:
- the Special Program to Support Corporate Financing,
- provision of yen and foreign currency funds without setting upper limits, and
- active purchases of ETFs and J-REITs.
Additionally, the Bank of Japan conducted an assessment for further effective and sustainable monetary policy at the meeting today. Based on the findings of this assessment, the Bank decided to continue with monetary easing in a sustainable manner and make effective responses to counter changes in development in economic activity and prices, as well as financial conditions.
To achieve that, the Bank will take the following actions:
- Establish the Interest Scheme to Promote Lending which will be linked to the short-term policy interest rate and will be applied to a certain amount of financial institutions' current account balances in order to enable the Bank to cut short- and long-term interest rates nimbly.
- Ensure that the range of 10-year Japanese government bond (JGB) yield fluctuations would be between around plus and minus 0.25 percent from the target level to conduct yield curve control flexibly during normal times. Additionally, the Bank will introduce "fixed-rate purchase operations for consecutive days" as a powerful tool to set an upper limit on interest rates when necessary.
- Purchase exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and Japan real estate investment trusts (J-REITs) as necessary with upper limits of about 12 trillion yen and about 180 billion yen, respectively, on annual paces of increase in their amounts outstanding even after the impacts of COVID-19 subsides.
Economic conditions in Japan continued to improve gradually throughout the end of 2020 and are expected to follow an improving trend with the impact of COVID-19 waning gradually. However, the pace of recovery is expected to be moderate due to the resurgence of COVID-19 in many countries. While private consumption has been on an upward trend, weak employment and income situation continues to put a downward pressure on consumption of services, such as eating and drinking as well as accommodations. Overall, the decline in business fixed investment has ended although uneven conditions among industries continues.
The year-over-year rate of the change in the consumer price index (CPI, all items less fresh food) is expected to be negative over the near term reflecting the impacts of COVID-19 and the past declines in oil prices. As the impacts of the decline in oil prices dissipate and economic recovery continues, the CPI is expected to turn positive and increase gradually.
The Bank noted that it will closely monitor the impacts of COVID-19 on the Japanese economy and is prepared to take additional easing measures as needed. The Bank expects short- and long-term policy interest rates to remain at their present or lower levels for the time being.
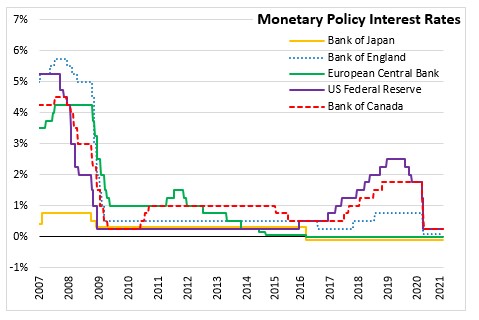
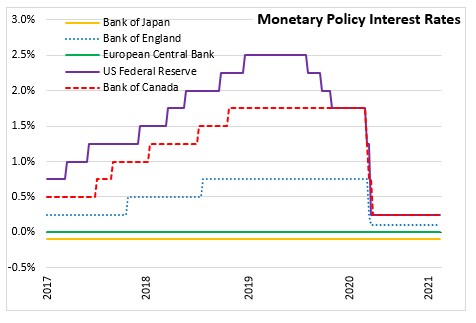
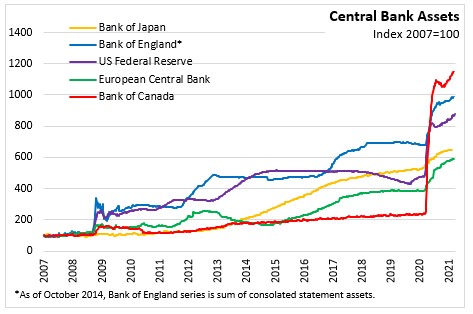
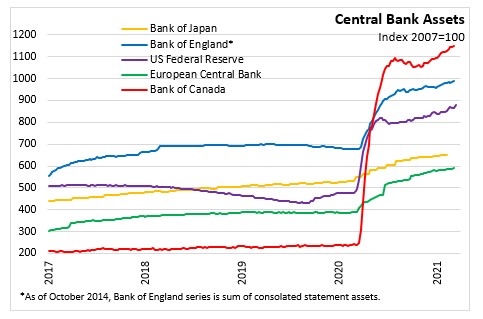

Source: Bank of Japan, Further Effective and Sustainable Monetary Easing
<--- Return to Archive