The Economics and Statistics Division maintains archives of previous publications for accountability purposes, but makes no updates to keep these documents current with the latest data revisions from Statistics Canada. As a result, information in older documents may not be accurate. Please exercise caution when referring to older documents. For the latest information and historical data, please contact the individual listed to the right.
<--- Return to Archive
For additional information relating to this article, please contact:
January 14, 2020JAPAN CURRENT ACCOUNT AND TRADE BALANCE, NOVEMBER 2019 Current Account
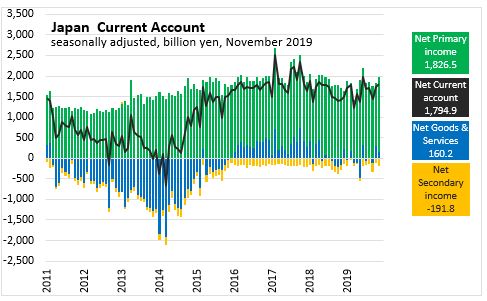
In November 2019, Japan reported
- Goods & services trade surplus narrowed by 141.4 billion yen to 160 billion yen
- Primary income surplus widened by 288 billion yen to 1,827 billion yen
- Secondary income deficit widened by 84 billion yen to 192 billion yen
- As a result, Current account surplus widened by 63 billion yen to 1,795 billion yen over October 2019.
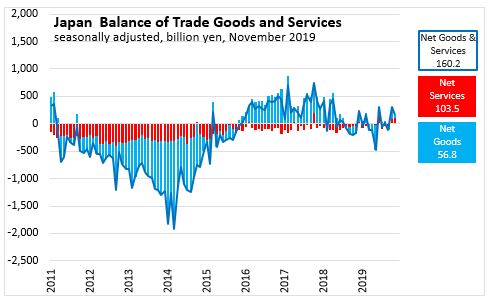
Trade Balance

In November 2019, Japan 's
- Export goods trade surplus narrowed by 217 billion yen to 6,192 billion yen
- Import goods trade surplus narrowed by 55 billion yen to 6,136 billion yen
- As a result, Net Goods trade surplus narrowed by 162 billion yen to 57 billion yen
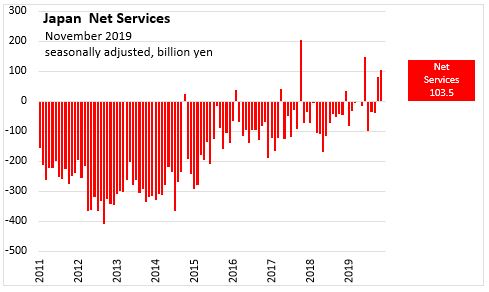
- Net Services trade surplus widened by 21 billion yen to 104 billion yen
- As a result, Goods & services trade surplus narrowed by 141.4 billion yen to 160 billion yen over October 2019.
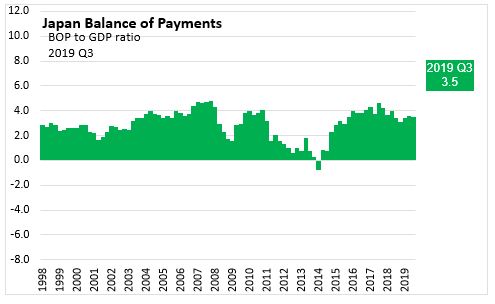
CURRENT ACCOUNT AS A SHARE OF GDP
The ratio of the current account balance to the Gross Domestic Product (or % of GDP) provides an indication of the country's trade and income flows relative to the size of the economy. The ratio is calculated by dividing the net values of exports less imports, primary Income (interest and dividends) and secondary income (transfers) over a period by the gross domestic product for the same period. Although called a ratio, it is usually expressed as a percentage. A current account surplus indicates upward pressure on the foreign exchange rate unless it is offset by net outflows (lending, acquisition of assets) outside the country.
- In the period 1999 Q1 to 2007 Q4, Japan’s current account to GDP measure was positive, ranging from 1.7% to 4.8%.
- With the recession in 2008-2009, Japan's current account to GDP measure declined to a low of 1.6% in 2009 Q1 but quickly recovered to a local high of 4.1% in 2010 Q4.
- Over the next 13 quarters (2011 Q4 to 2014 Q1), Japan’s current account to GDP measure declines 3.9 points to -0.7%.
- Over the next 14 quarters (2014 Q1 to 2017 Q3), Japan’s current account to GDP measure recovered to a new local high of 3.56% in 2017 Q3.
- In the period to 2019 Q3, Japan's current account to GDP measure has declined 0.7 points to 3.5%.
Report | Press Release | Balance of Payments
Based on Table 6s-a-2 Current Account (seasonally adjusted), Monthly
OECD BOP as a % of GDP
<--- Return to Archive